Physiotherapy is very important during the rehabilitation following a femoral condyle fracture. The medial condyle is larger than the lateral outer condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the centre of mass being medial to the knee.
Ad Ligaments are all around your body such as your knees elbows shoulders and ankles.
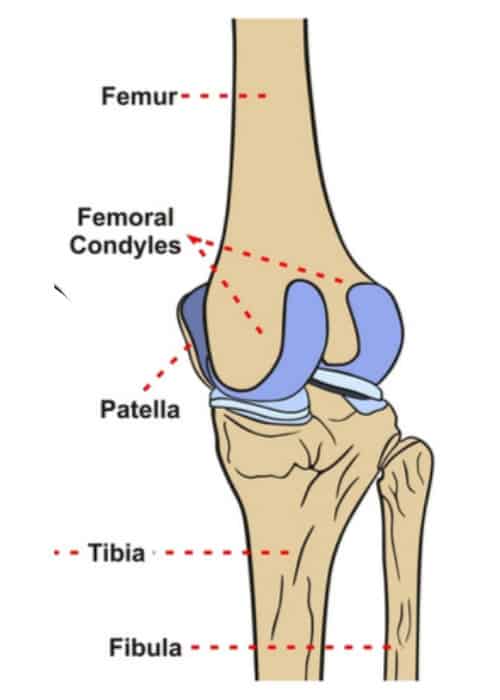
. Tibial crest medial malleolus Fibula head Shaft lateral malleolu. Interface of the medial and lateral femoral condyles. The medial condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of femur the other being the lateral condyle.
The medial condyle is larger than the lateral outer condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the centre of mass being medial to the knee. The articular cartilage thickness on the medial posterior femoral condyle was 3 mm 1 mm mean standard deviation and 1 mm 1 mm on the lateral side p-value. The femoral condyles articulate or contact with the tibia and on the medial side this is in the medial tibial plateau and the medial meniscus and on the outside of the knee is known as the lateral tibial plateau in the.
Which femoral condyle is wider transversely. While both bones feature a medial and lateral condyle with the lateral condyle on the other side of the knee the medial condyle is the larger prominence because more weight is transferred across the inside aspect of the knee joint. In the 155 varus knees the radius of the lateral condyle was an average of 01 mm larger than that of the medial condyle p 0003.
Head of the fibula e. Most people injure their ligaments through physical activity accidents or wear and tear. The medial and lateral condyles form the proximal part of the body of femur and articulate with the proximal part of tibia to form the femorotibial joint.
If there is a fracture break in part of the condyle this is known as a fracture of the femoral condyle. Medial femoral condyle is larger than lateral condylethis helps when viewing the knee on lateral or axial patellar projections Suprapatellar recessrecess between the suprapatellar tendon and the anterior cortex of the femur normally relatively radiolucent. Which bone does not.
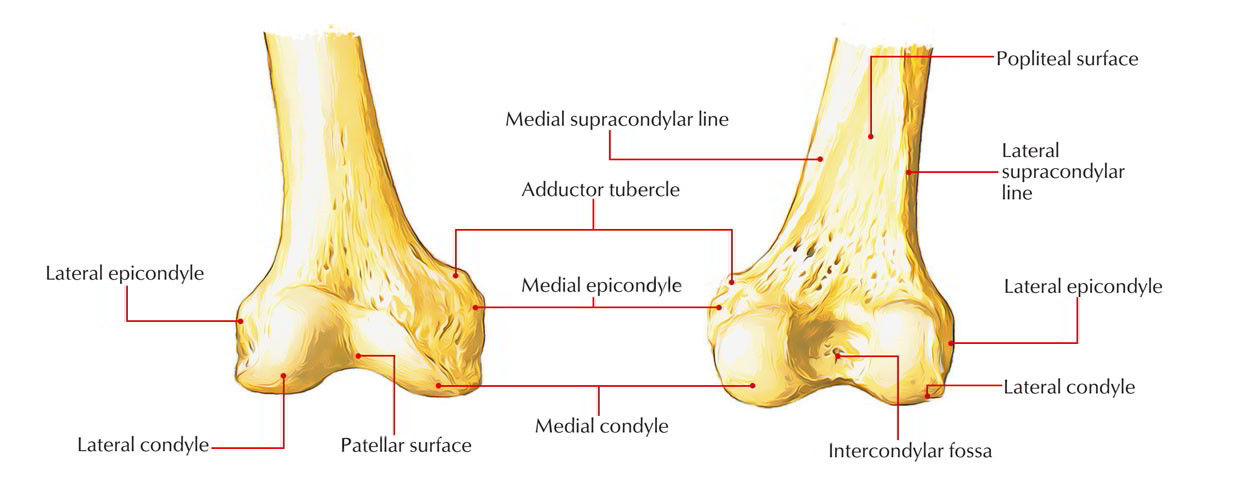
Patellar surface popliteal surface Patella Base Apex SHANK Tibia medial lateral condyles tibial tuberosity. The motions of the condyles include rocking gliding and rotating. The study provided a reliable and consistent evaluation of the coronal curvature of femoral condyles in the Korean population.
The femoral condyles are the two rounded prominences at the end of the femur. The tuberosity of the tibia or tibial tuberosity or tibial tubercle is a large oblong elevation on the proximal anterior aspect of the tibia just below where the anterior surfaces of the lateral and medial tibial condyles end. Medial and lateral condyles rounded areas at the end of the femur.
The distal end of the femur is characterised by the presence of the medial and lateral condyles which articulate with the tibia and patella to form the knee joint. The medial condyle is larger than the lateral outer condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the centre of mass being medial to the knee. The medial and lateral condyles of the tibia articulate with the a.
A femoral condyle is the ball-shape located at the end of the femur thigh bone. Palpable as a hard rounded bump to the inside of either knee joint they are one of two condyles at the bottom of each leg bone the other being the lateral femoral condyle. Furthermore the medial and lateral coronal curvatures of the femoral condyle were symmetric in all TKA implant designs.
They are the pair of rounded eminences that form the. The paired femoral condyles are situated to either side of the patella or kneecap. There is a significant difference in articular cartilage thickness between the medial and lateral posterior femoral condyles in patients undergoing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty.
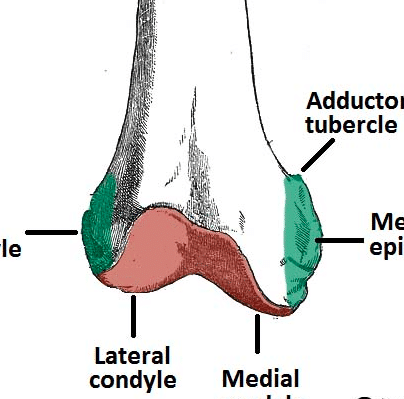
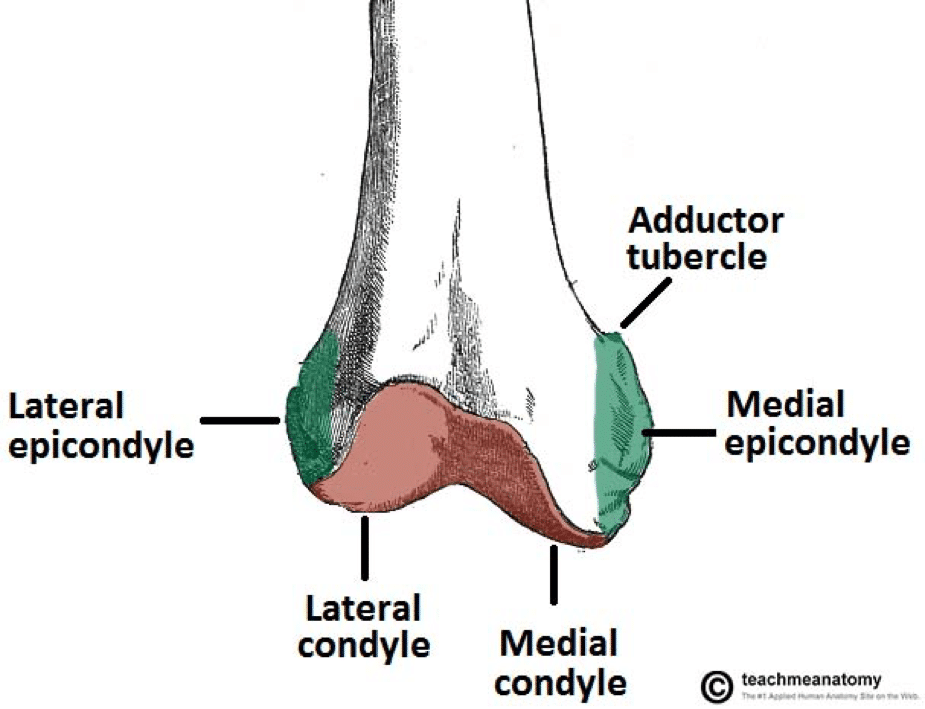
In between the medial and lateral femoral condyles is the intercondylar fossa. Medial and lateral condyles of the femur c. There are two condyles on each leg known as the medial and lateral femoral condyles.
Anatomical terms of bone. They are separated by the deep intercondylar fossa proximally bounded by the horizontal intercondylar line. The medial condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of femur the other being the lateral condyle.
Any abnormal surface structure or cartilage damage can lead to cartilage breakdown and arthritis loss of cartilage padding. The medial femoral condyle is located on the inside part of the knee whereas the lateral femoral condyle which is bigger is located on the outside part of the knee. Greater and lesser trochanters of the femur.
Medial and lateral condyles of the femur are involved in the hip joint. The lateral condyle is the more prominent and is the broader both in its antero-posterior and transverse diameters the medial condyle is the longer and when the femur is. They are called the medial and the lateral femoral condyle respectively.
The medial femoral condyles are the bony protrusions on the inside edge of the bottom of the femur bone in each thigh. The medial condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of femur the other being the lateral condyle. The most accurate equation used width of the medial and lateral condyles WDC with of the medial condyle WMC depth of the lateral condyle DLC and depth of the intercondylar notch DIN 941 and is as follows.
The radius of a condyle was the average of the radii on four adjacent images that showed the femoral condyle with the largest curvature. Medial and lateral epicondyles of the femur d. Apex of the patella b.
While degenerative changes to the articular cartilage of the anterior and distal portions of the femoral condyles have been well studied in the litera. D 0336 WDC -0097 WMC -0153 DLC 0372 DIN - 20912. On the posterior surface of the condyle the linea aspera a ridge with two lips.
These results showed that a gender-specific or asymmetric femoral component design is required to regenerate the coronal. Learn more about the femur in this. THIGH మమల Femur head neck greater trochanter lesser trochanter Shaft linea aspera medial condyles lateral condyles.
The medial condyle is larger than the lateral outer condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the center of gravity being medial to the knee. On each condyle is a smaller epicondyle which serve as the point of attachment for the collateral ligaments the medial collateral MCL and the lateral collateral ligaments LCL. Asked Sep 28 2016 in Anatomy Physiology by helpmeout.
The medial condyle is larger than the lateral outer condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the centre of mass being medial to the knee. The posterior and inferior surfaces articulate with the tibia and menisci of the knee while the anterior surface articulates with the. The medial condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of femur the other being the lateral condyle.
At the end of the medial supracondylar line is a tubercle called the adductor tubercle. The medial condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of femur.

Femur An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Medial Condyle Of Femur Wikipedia
Orif Lag Screw For Lateral Medial Femoral Epicondyle Fracture
Distal Femur Fracture Teachmesurgery
Distal Femur Fracture Teachmesurgery

Femoral Condyle Articular Cartilage Injury Minneapolis St Paul Edina Eagan Mn

0 komentar
Posting Komentar